| 1900-1945 |
 |
 | 1900 |
 |
 | ・義和団事件 The Boxer Rebellion attempted to drive out all foreigners from China. |
 |
 | 1901 |
 |
 | ・北京議定書 The Beijing Protocol, which officially ended the Boxer Rebellion, further subjugated China to foreign imperialism. |
 |
 | 1904 |
 |
 | ・英仏協商 The Anglo-French Entente (the Entente Cordiale), which, together with the Anglo-Japanese Alliance (日英同盟) of 1902, marked the end of the British policy of “splendid isolation” (光栄ある孤立). The agreement also signified the end of the Anglo-French rivalry that had lasted for centuries. |
 |
 | 1905 |
 |
 | ・血の日曜日事件 Bloody Sunday. Soldiers in St. Petersburg fired at a procession of workers, signaling the start of the First Russian Revolution (第一次ロシア革命). |
 |
 | ・第一次モロッコ事件 The First Moroccan Crisis. The German Emperor landed in Morocco, then held by the French. |
 |
 | 1907 |
 |
 | ・英露協商により英・仏・露の三国協商完成 The Anglo-Russian Entente completed the three bilateral treaties of the Triple Entente among Britain, France, and Russia. |
 |
 | 1911 |
 |
 | ・第二次モロッコ事件 The Second Moroccan Crisis. The Germans sent a gunboat to Agadir. |
 |
 | ・辛亥革命 The Republican Revolution in China. |
 |
 | 1912 |
 |
 | ・清朝滅び, 中華民国成立 The Qing Dynasty fell and the Republic of China was founded. Sun Yat-sen (孫逸仙=孫文) handed over the leadership to Yuan Shikai (袁世凱). |
 |
 | 1912-13 |
 |
 | ・バルカン戦争 The Balkan Wars. |
 |
 | 1914 |
 |
 | ・サラエボ事件を契機に第一次世界大戦勃発 Archduke Francis Ferdinand (フランツ・フェルディナント) of Austria and his wife were assassinated by a Serbian nationalist student at Sarajevo, triggering World War I. |
 |
 | 1915 |
 |
 | ・フサイン・マクマホン協定 In the McMahon Correspondence, Britain promised the Arab leader Husayn support for Arab independence after the war. |
 |
 | 1916 |
 |
 | ・サイクス・ピコ協定 The Sykes-Picot Agreement partitioned the Middle East between Britain and France. |
 |
 | ・ロシアの怪僧ラスプーチン暗殺 Rasputin, called the Mad Monk, was assassinated. |
 |
 | 1917 |
 |
 | ・ロシア革命 The Russian Revolution. |
 |
 | ・二月革命 The February Revolution (the March Revolution according to the Gregorian calendar). Tsar Nicholas II (ニコライ 2 世) abdicated and Kerensky (ケレンスキー) took over the government. |
 |
 | ・コルニーロフの反乱 The Kornilov Affair. General Kornilov revolted and Kerensky turned for support to the Bolsheviks (ボルシェヴィキ). |
 |
 | ・十月革命 The October Revolution (the November Revolution according to the Gregorian calendar). The Bolsheviks led by Lenin (レーニン) seized power. |
 |
 | ・バルフォア宣言 The Balfour Declaration. The British foreign minister pledged support for the establishment of a Jewish state in Palestine. |
 |
 | 1918 |
 |
 | ・ブレスト・リトフスク条約 The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk. The Bolsheviks made peace with the Germans. |
 |
 | ・ドイツ, オーストリアで帝政崩壊し停戦 Armistice was agreed after the collapse of the imperial regimes in Germany and Austria. |
 |
 | 1919 |
 |
 | ・中国で五・四運動 The May Fourth Movement in China. |
 |
 | ・ヴェルサイユ条約 The Treaty of Versailles was signed to end World War I. |
 |
 | ・ワイマール共和国成立 The Weimar Republic was established in Germany with the democratic Weimar Constitution (ワイマール憲法). |
 |
 | 1920 |
 |
 | ・国際連盟成立 The League of Nations was founded. |
 |
 | 1922 |
 |
 | ・北部を除くアイルランドが自治領に Ireland, except for Ulster, gained the status of a dominion as the Irish Free State (アイルランド自由国). |
 |
 | ・ソビエト連邦成立 Formation of the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (USSR). |
 |
 | 1923 |
 |
 | ・トルコ共和国成立 The Republic of Turkey was established in place of the sultanate. Kemal Atat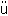 rk (ケマル・アタテュルク) became the first president. rk (ケマル・アタテュルク) became the first president. |
 |
 | 1924 |
 |
 | ・レーニン没し, スターリンによる革命の変質始まる Lenin died. The Soviet regime would be transformed by Stalin. |
 |
 | ・第一次国共合作 Cooperation between the Kuomintang (国民党), founded by Sun Yat-sen, and the Communist Party of China (中国共産党). |
 |
 | 1925 |
 |
 | ・イランでパーレヴィ朝成立 The Pahlavi dynasty was established in Persia (to be officially renamed Iran in English in 1935). |
 |
 | 1926-28 |
 |
 | ・蒋介石の北伐 Chiang Kai-shek, the successor to Sun Yat-sen, set out on the Northern Expedition and secured control of all of China. |
 |
 | 1929 |
 |
 | ・世界恐慌 The Great Depression set in with the crash of the US stock market. |
 |
 | 1931 |
 |
 | ・ウエストミンスター憲章 The Statute of Westminster confirmed equal status for Britain and the dominions of the British Commonwealth (イギリス連邦) (the Irish Free State, Canada, Newfoundland, Australia, the Union of South Africa, and New Zealand). |
 |
 | 1933 |
 |
 | ・ヒトラーの政権掌握 Adolf Hitler, the leader of the Nazi party, became chancellor (首相) under President Hindenburg (ヒンデンブルク大統領) and soon seized power. |
 |
 | ・日・独, 国際連盟脱退 Japan and Germany left the League of Nations. |
 |
 | 1934 |
 |
 | ・ヒトラー総統に President Hindenburg died and Hitler became f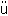 hrer and chancellor, abolishing the title of president. hrer and chancellor, abolishing the title of president. |
 |
 | 1934-36 |
 |
 | ・紅軍の長征(大西遷) The Chinese Red Army set out on the Long March to the west and north, fleeing from the Kuomintang army. Mao Zedong (毛沢東) attained leadership during the march. |
 |
 | 1936-39 |
 |
 | ・スペイン内乱 The Spanish Civil War. The military, led by General Francisco Franco (フランコ) and assisted by Germany and Italy, established a dictatorship, defeating the Popular Front (人民戦線) supported by the Soviet Union and republican volunteers. |
 |
 | 1937 |
 |
 | ・アイルランド, エールとして独立を宣言 Ireland declared independence as the state of Eire. |
 |
 | 1938 |
 |
 | ・ミュンヘン会談 The Munich Conference. |
 |
 | 1939 |
 |
 | ・独ソ不可侵条約 The German-Soviet Nonaggression Pact. |
 |
 | ・第二次世界大戦勃発 The German invasion of Poland started World War II. |
 |
 | 1940 |
 |
 | ・日独伊三国同盟 The Tripartite Pact among Japan, Germany, and Italy. |
 |
 | 1943 |
 |
 | ・ムッソリーニ罷免され, イタリア降伏 After the king's dismissal of Mussolini, Italy surrendered to the Allies. |
 |
 | 1945 |
 |
 | ・ヒトラー自殺し, ドイツ降伏 After Hitler's suicide, Germany surrendered. |
 |
 | ・チトー, ユーゴスラヴィアをドイツ軍から解放 Marshal Tito led partisans and freed Yugoslavia from the Germans. |
 |
 | ・国際連合設立 The United Nations was founded. |
 |
 | ・広島・長崎への原爆投下 The United States dropped atomic bombs on Hiroshima and Nagasaki. |
 |
 | ・日本ポツダム宣言を受諾し降伏. 昭和天皇終戦を宣す Japan surrendered by accepting the Potsdam Declaration. Hirohito announced the end of the war on radio. |
 |
 |
|
 |
 |
|